By Renova Hospitals
November 18, 2025
Cachexia: Extreme Weight Loss, Muscle Wasting & Metabolic Imbalance – Complete Guide by Renova Hospitals Hyderabad
What Is Cachexia? A Medically Detailed Explanation
- Involuntary weight loss
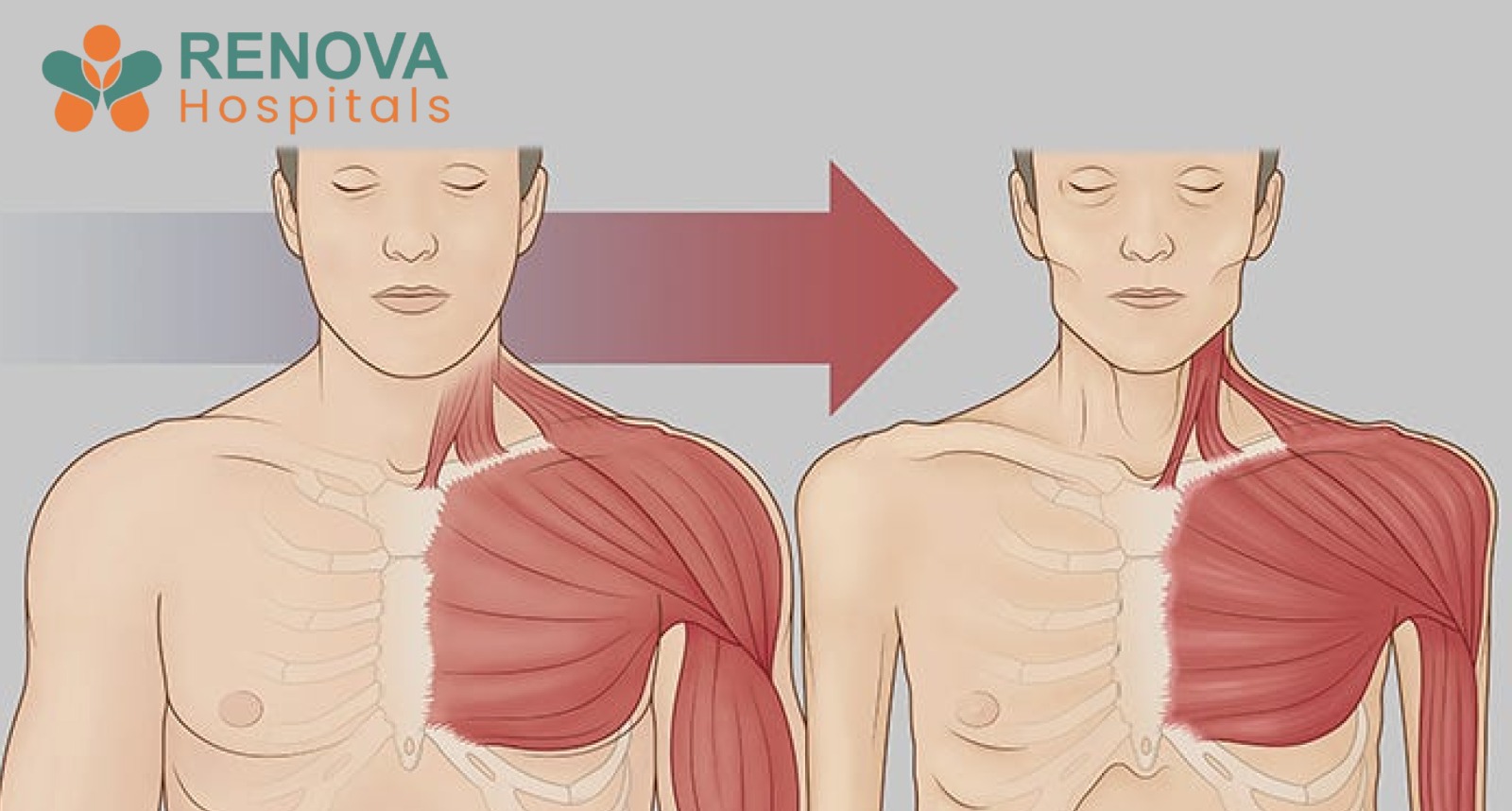
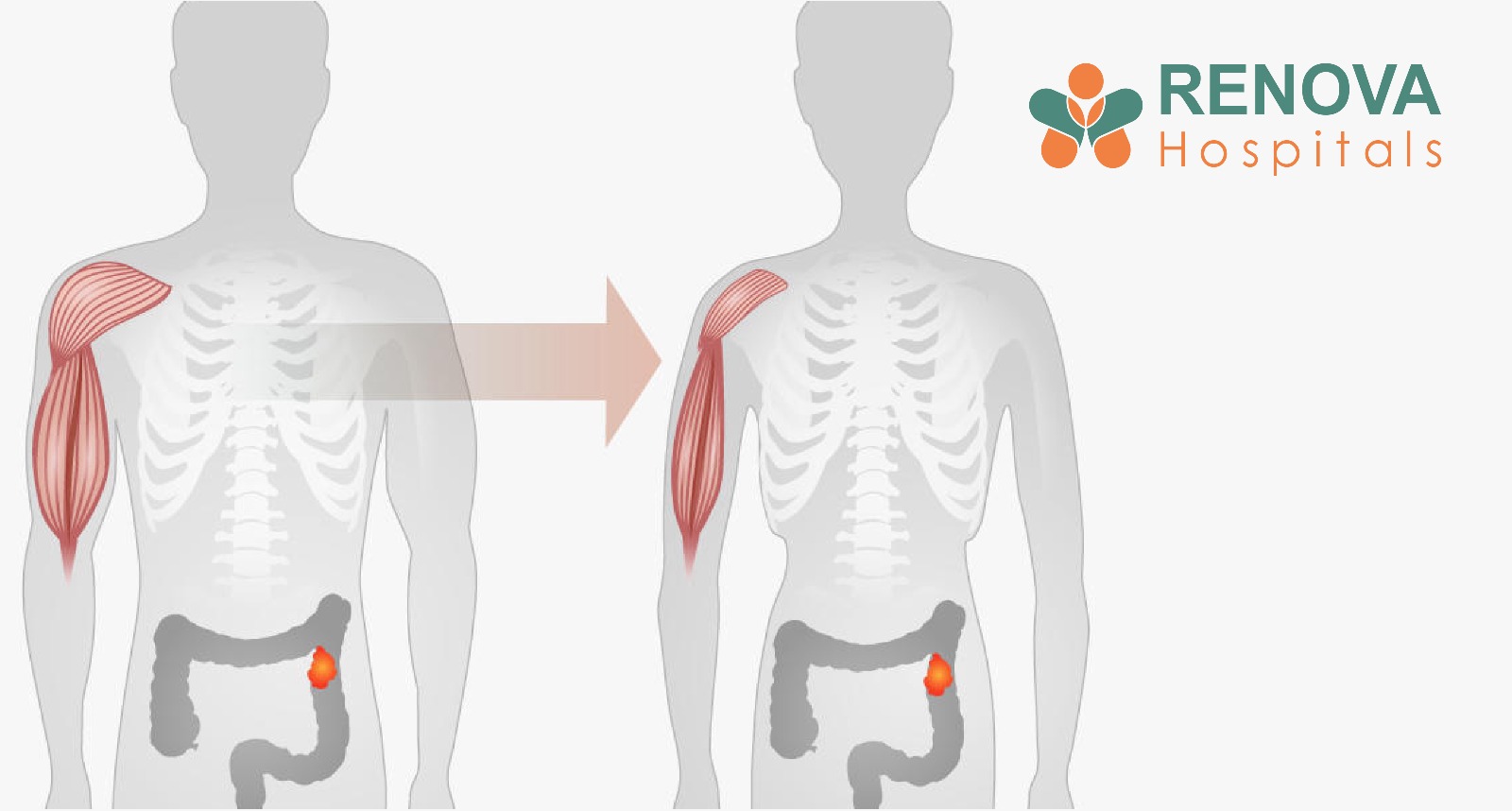
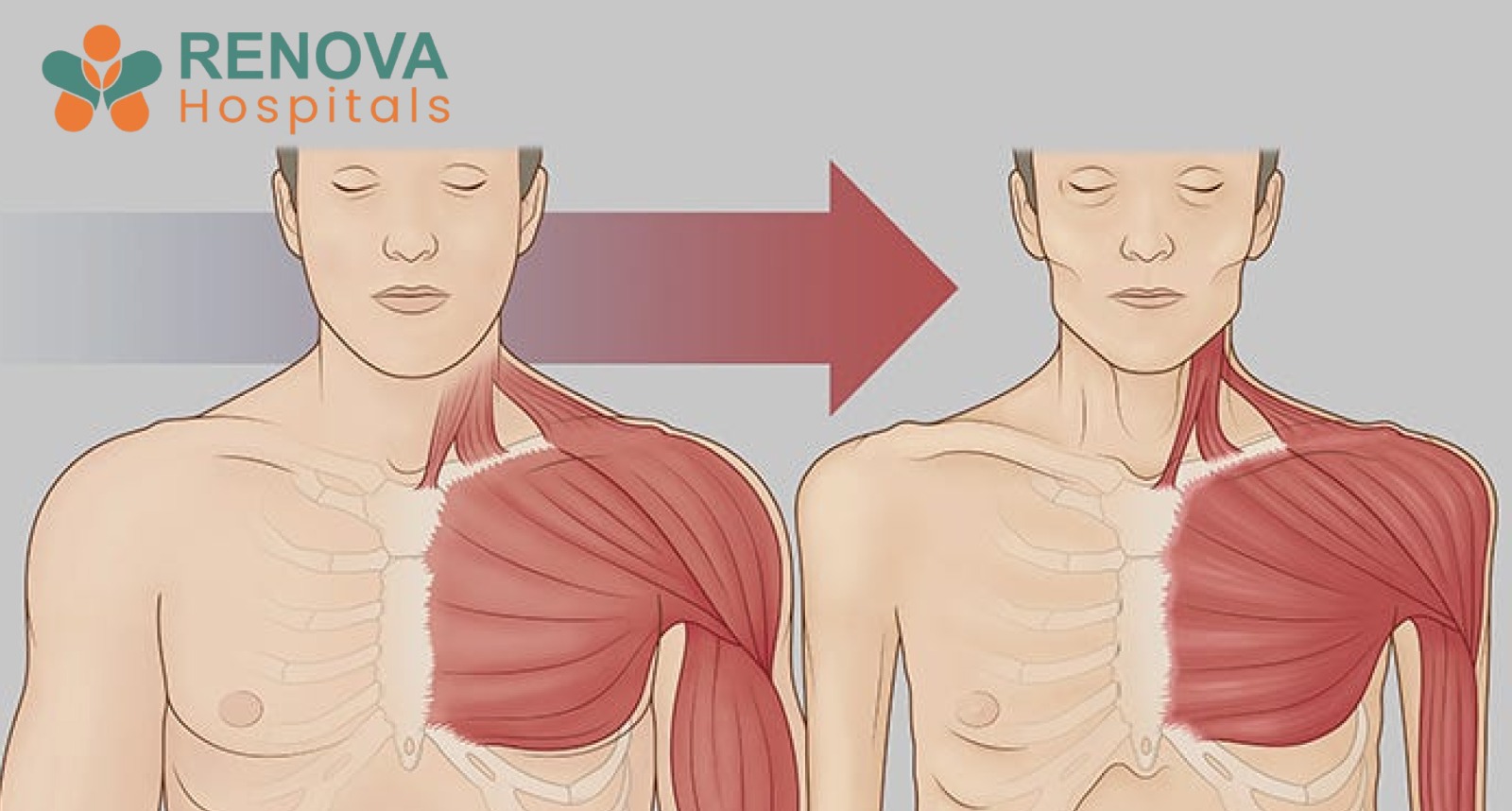
- Severe muscle wasting (sarcopenia)
- Loss of body fat
- Reduced appetite (anorexia)
- Increased energy expenditure
- Inflammation that disrupts normal metabolism
Stages of Cachexia
Cachexia progresses through three medically recognised stages:
- Small but noticeable weight loss
- Reduced appetite
- Mild inflammation
- Early change in metabolism
2. Cachexia (Active Stage)
- >5% weight loss in 6 months OR
- 2% weight loss + low muscle mass
- Pronounced weakness
- Loss of skeletal muscle
- Fatigue and decreased functional ability
- Severe muscle loss
- Low performance status
- Poor response to nutrition or medication
- Occurs in end-stage illness
Cachexia Causes: Why the Body Breaks Down Muscle and Fat
1. Chronic Inflammation
- TNF-α (Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha)
- IL-6 (Interleukin-6)
- IL-1β
3. Hormonal Dysfunction
- Low testosterone
- Insulin resistance
- High cortisol (stress hormone)
- Low growth hormone and IGF-1
6. Digestive and Metabolic Impairment
Types of Cachexia
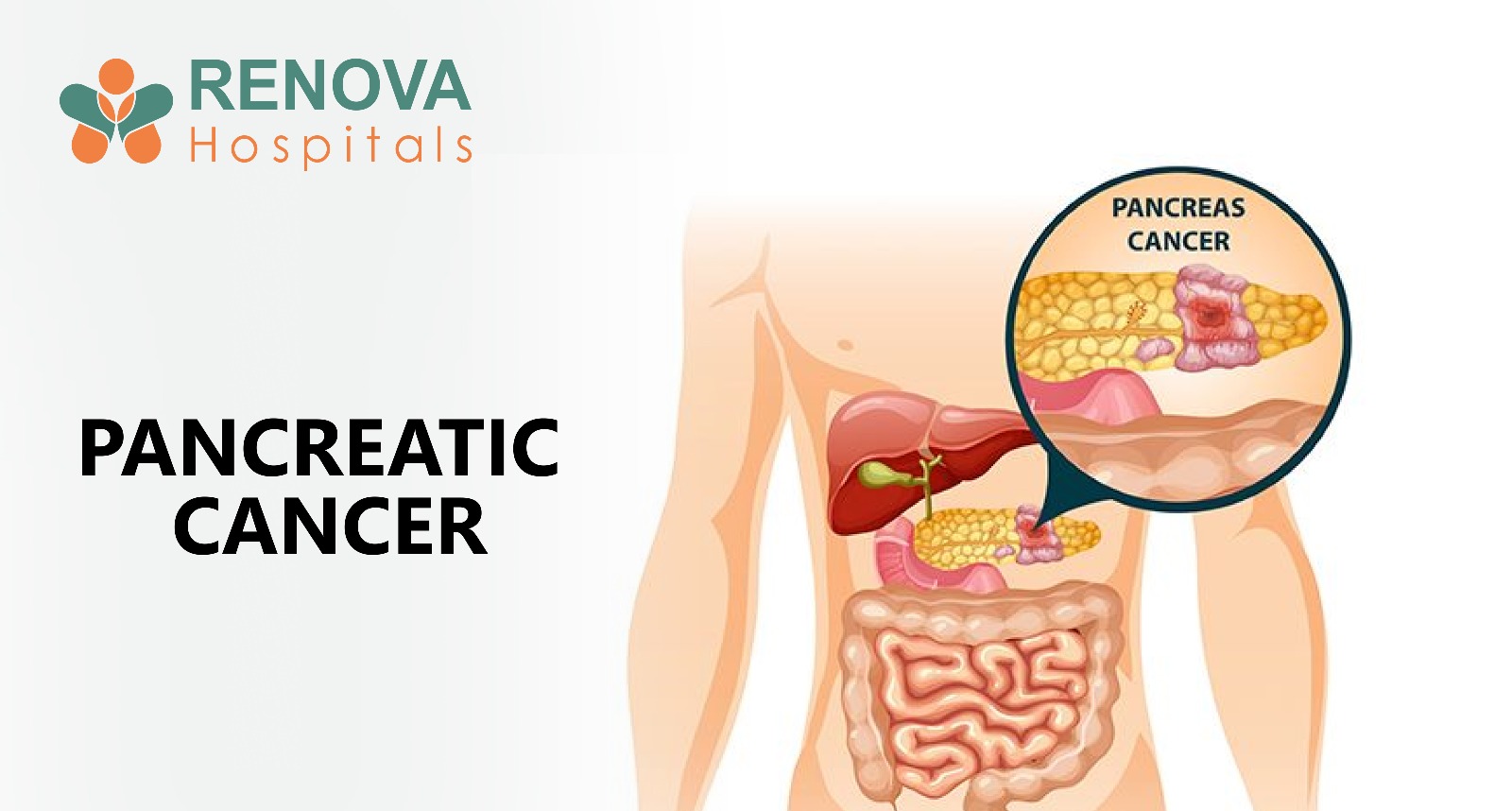
- Pancreatic cancer
- Gastric cancer
- Lung cancer
- Colon cancer
- Esophageal cancer
- Liver cancer
- Advanced head and neck cancers
- Extreme muscle wasting
- Fatigue despite rest
- Intolerance to chemotherapy
- Taste changes
- Inflammation-driven anemia
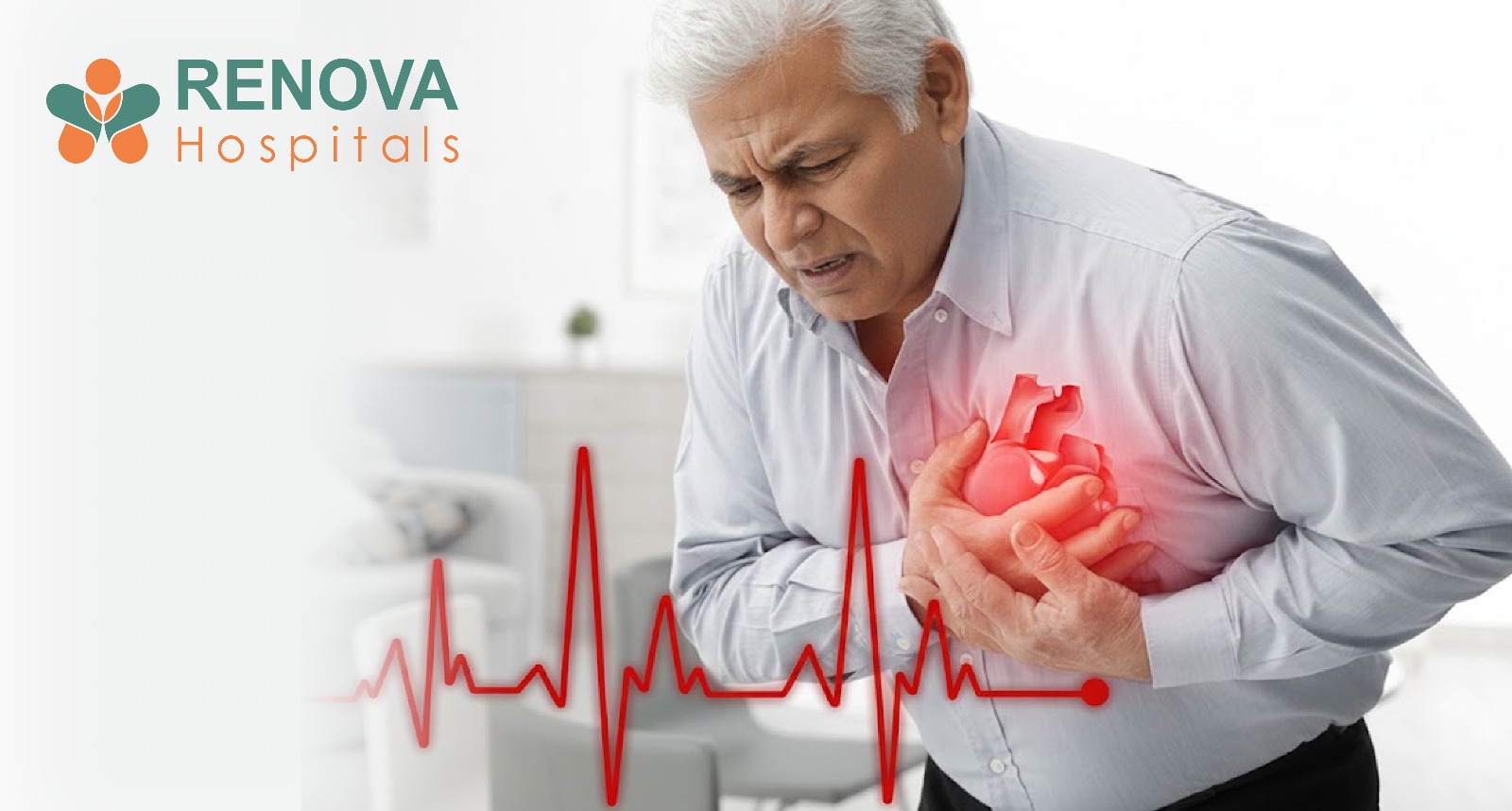
2. Cardiac Cachexia (Heart Failure–Associated Muscle Wasting)
Seen in end-stage congestive heart failure (CHF).
- Reduced blood supply to muscles
- Poor nutrient absorption
- Increased metabolism to maintain heart function
- Hormonal disruption (high cortisol & catecholamines)
- Severe fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Fluid retention in legs
- Breathlessness
- Unexplained weight loss
3. Renal Cachexia (Chronic Kidney Disease–Related)
- Uremic toxins suppress appetite
- Metabolic acidosis accelerates muscle breakdown
- Dialysis causes loss of amino acids
- Chronic inflammation
- Low albumin levels
- Muscle wasting
- Swelling
- Loss of appetite
- Metallic taste
- Nausea and vomiting
Seen in chronic lung diseases like:
- COPD
- Emphysema
- Advanced asthma
- Cystic fibrosis
- Increased energy used for breathing
- Chronic hypoxia (low oxygen) damages muscle fibres
- Inflammation from repeated infections
- Poor appetite due to breathlessness
- Skinny limbs
- Breathlessness during minimal activity
- Weakness
- Inability to gain weight
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Liver cancer
- Poor nutrient absorption
- Inability to store glycogen
- Altered metabolism of protein and fat
- High ammonia levels reduce appetite
- Severe weight loss
- Muscle cramps
- Ascites
- Edema
- Altered taste
6. Gastrointestinal Cachexia (Malabsorption-Related)
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Short bowel syndrome
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Celiac disease
- Malabsorption
- Nutrient loss in stool
- Chronic abdominal pain reduces appetite
- Inflammation-driven muscle loss
- Unexplained diarrhea
- Weight loss despite eating
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Muscle thinning
- Tuberculosis
- HIV/AIDS
- Long-term fungal infections
- Malaria
- Chronic hepatitis
- Sepsis survivors
- Persistent inflammation
- High energy demands
- Appetite suppression
- Protein breakdown to fuel immune response
- Extreme fatigue
- Weakness
- Night sweats
- Rapid weight loss
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Vasculitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Weight loss
- Chronic pain
- Stiffness
- Weakness
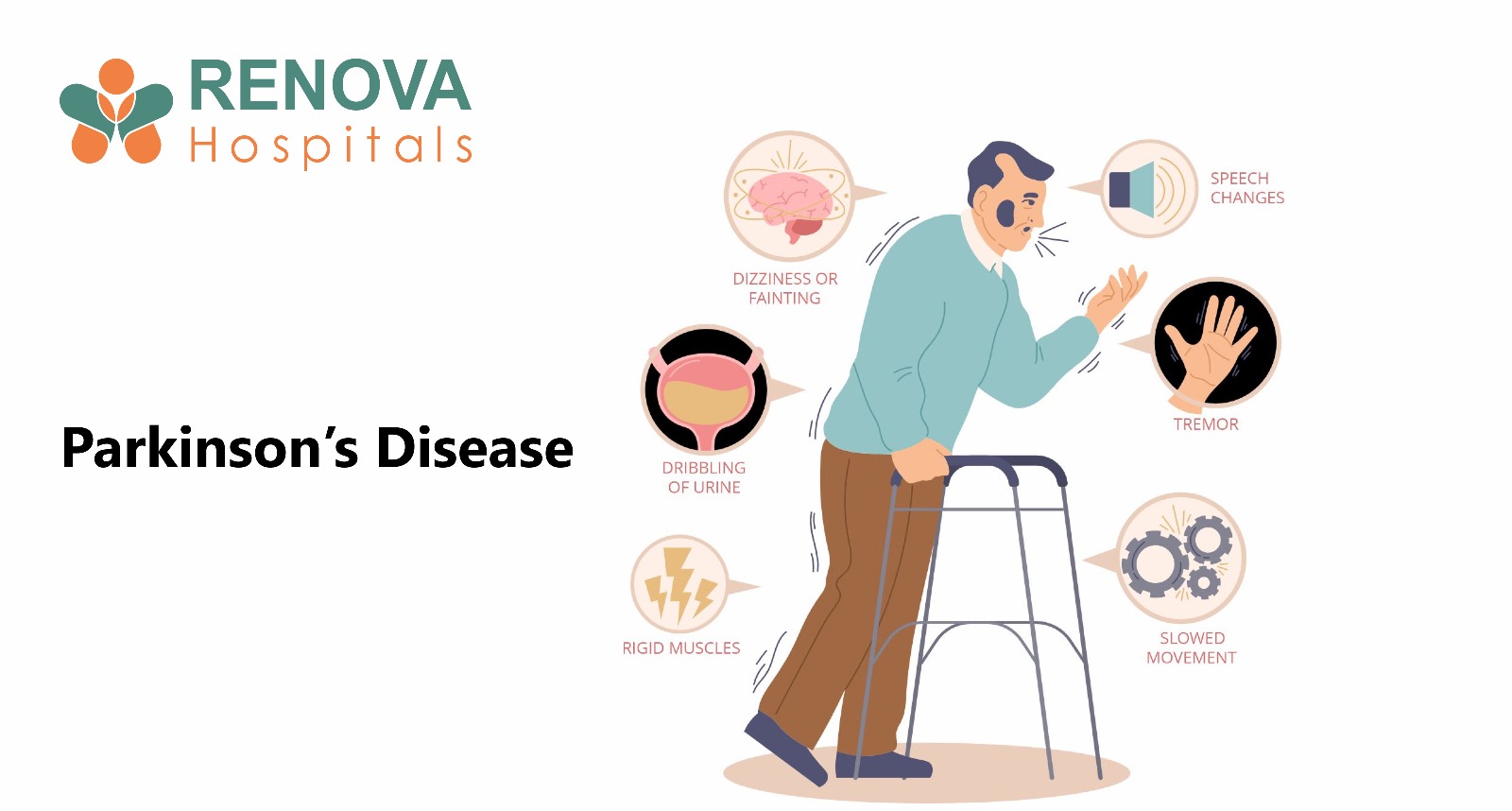
- Parkinson’s disease
- ALS
- Dementia
- Multiple sclerosis
- Increased metabolic demand
- Difficulty swallowing
- Decreased mobility
- Depression and feeding difficulty
- Rapid muscle loss
- Swallowing issues
- Drooling
- Fatigue
Occurs in elderly adults due to:
- Declining appetite
- Hormonal changes
- Sarcopenia
- Inflammation
- Chronic illness
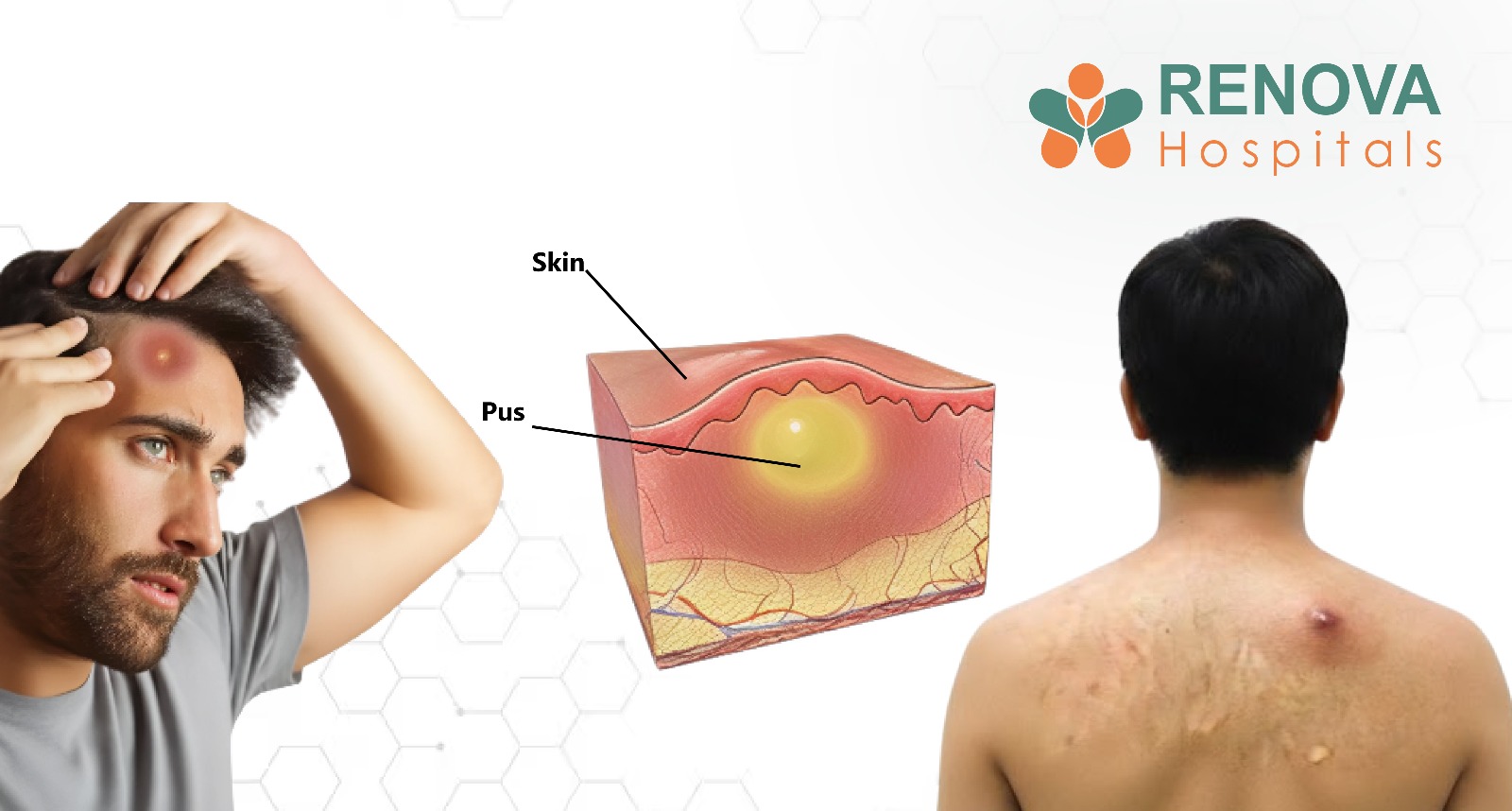
Cachexia Symptoms: Detailed Breakdown
Physical Symptoms
- Rapid weight loss
- Visible ribs, collarbones, and shrinking limbs
- Loss of muscle strength
- Thinning of arms and thighs
- Fatigue even after rest
- Reduced appetite
- Early fullness
- Taste changes (metallic taste)
- Aversion to meat or protein foods
- Nausea or vomiting in cancer patients
- Elevated inflammatory markers
- Anemia
- Low albumin and protein levels
- Oedema (swollen legs)
- Increased resting heart rate
- Difficulty standing or climbing stairs
- Low exercise tolerance
- Dependence on caregivers for daily tasks
- Depression
- Anxiety around food
- Social withdrawal
- Irritability
How Cachexia Is Diagnosed at Renova Hospitals, Hyderabad
Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, body composition tests, and metabolic assessment.
- Weight changes
- Muscle strength loss
- Chronic disease evaluation
- Appetite assessment
- DEXA Scan – gold standard for measuring muscle and fat mass
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
- CT-scan muscle density measurement
- CRP, IL-6, ESR (inflammation markers)
- Albumin and prealbumin
- Hemoglobin levels
- Liver and kidney function
- Hormonal profile (testosterone, thyroid, IGF-1)
4. Functional Assessment
- Grip strength
- Walking tests
- Repeated sit-to-stand assessments
Conducted by Renova’s clinical nutrition experts to evaluate caloric, protein, and micronutrient intake.
Cachexia Treatment: Renova Hospitals Multidisciplinary Approach
- Energy-dense foods
- High protein intake (1.2–2 g/kg/day)
- Omega-3-rich foods
- Easy-to-digest meals
- Appetite-friendly flavors
Renova uses therapeutic formulations containing:
- Whey protein
- BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine, valine)
- Omega-3 (EPA/DHA)
- Vitamin D, zinc, and antioxidants
For patients who cannot eat due to illness or treatment side effects:
- Tube feeding (NG/PEG) with specialised formulas.
- Megestrol acetate
- Corticosteroids
- Mirtazapine (helps mood and appetite)
- NSAIDs or COX-2 inhibitors
- Omega-3 supplements for cytokine suppression
- Testosterone replacement
- Growth hormone analogues
- Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs – under supervision)
Gastrointestinal Medications
- Prokinetics to improve digestion
- Anti-nausea drugs (ondansetron, aprepitant)
At Renova, physiotherapy plays a crucial role:
- Resistance training to rebuild muscle
- Aerobic conditioning to improve stamina
- Stretching for flexibility
- Bedridden patient mobility support
- Counseling
- Art and music therapy
- Family support groups
- Stress management sessions
- Cancer
- Heart failure
- Kidney failure
- COPD
- Tuberculosis
- Liver disease
- Severe frailty
- Organ failure
- Poor wound healing
- Infections and sepsis
- Intolerance to chemotherapy
- High hospital readmission
- Increased mortality
Nutrition & Home Care Tips for Cachexia Patients
Renova’s dietitians help families prepare culturally familiar, nutritious meals suitable for cachexia patients.
- Eat 6–8 small meals daily
- Add extra ghee, butter, or olive oil to foods
- Choose high-protein snacks (paneer, eggs, yoghurt)
- Try cold foods if nausea is severe
- Sip nutrient shakes throughout the day
- Avoid drinking large amounts of water before meals
- Engage in light walking or physiotherapy exercises
- Maintain emotional support and encouragement
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
- Muscle strength
- Appetite
- Energy
- Better tolerance to medical treatments
Renova Hospitals Hyderabad: Expert Care for All Types of Cachexia
Renova’s centres in Banjara Hills, Secunderabad, Kompally, and Warangal offer end-to-end care for cancer cachexia, cardiac cachexia, renal cachexia, pulmonary cachexia, infectious cachexia, and geriatric cachexia.
Partially, yes, especially in the early stages. Advanced cachexia is difficult but can be stabilised.
2. Can eating more cure cachexia?
No. Cachexia requires medical, nutritional, and metabolic treatment.
Severe muscle wasting caused by cancer-related inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.
Yes. Up to 80% of advanced cancer patients develop it.
Supervised physiotherapy slows muscle loss and improves strength.
Category
- Joint Replacement
- Joint Replacement
- Joint Replacement