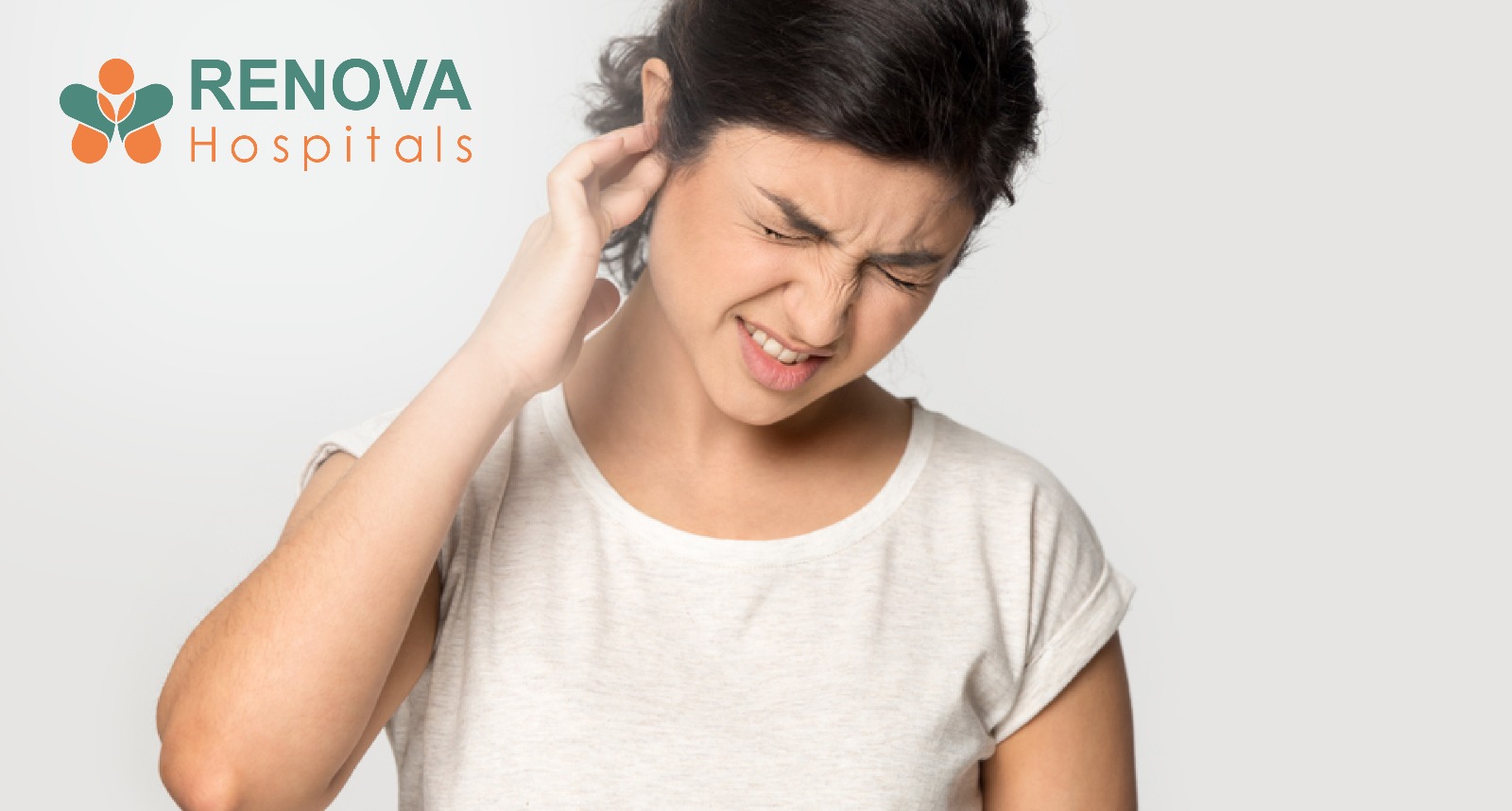
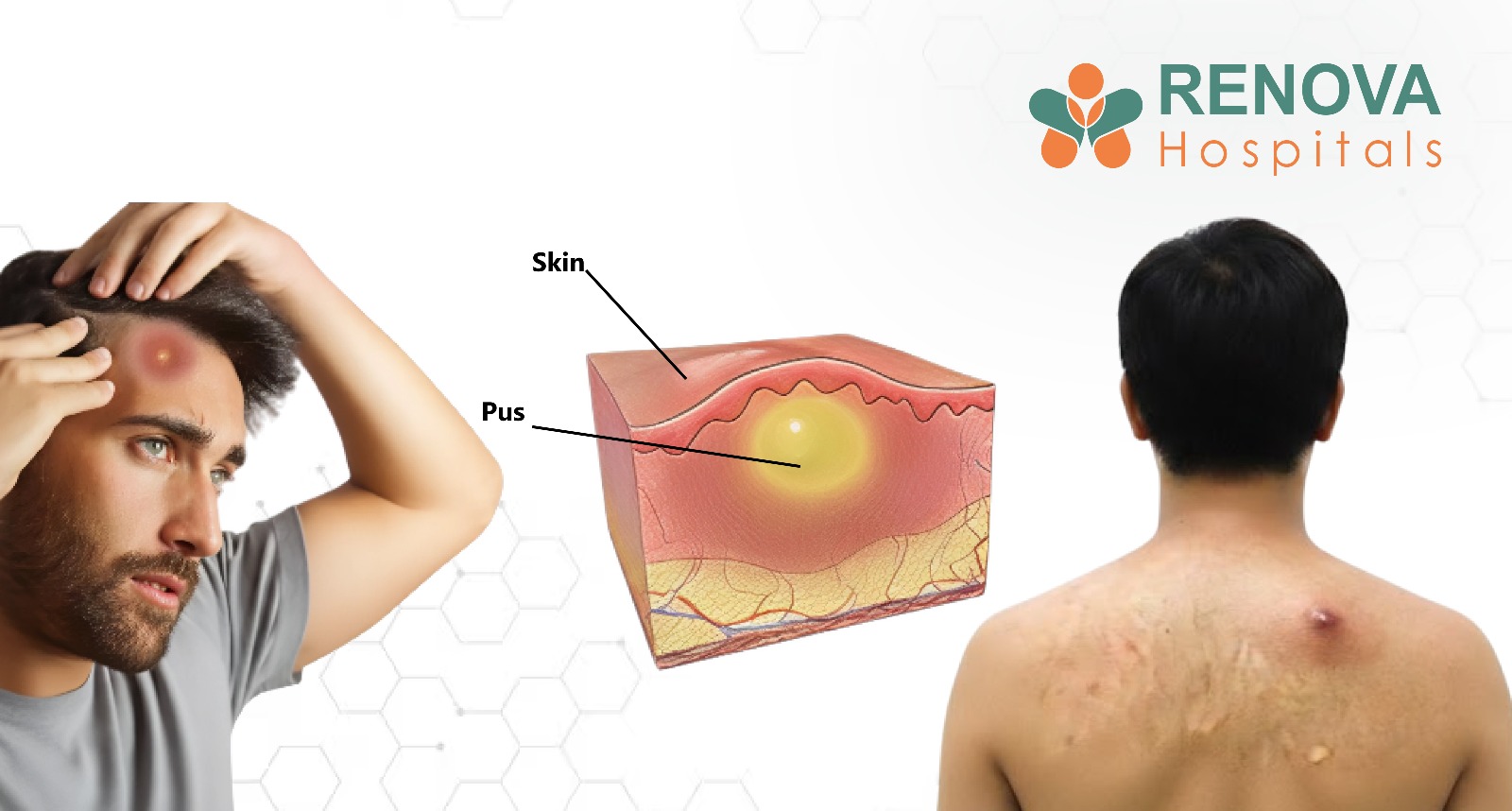
Dandruff, or medically seborrhea / seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, is one of the world’s most common scalp disorders. Despite being common, it is frequently misunderstood.
Many believe dandruff is simply dry skin, but in reality, seborrheic dermatitis scalp is a chronic inflammatory condition involving increased oil production, fungal imbalance, irritation, and disruption of the scalp’s protective barrier.
The condition can be mild or severe, ranging from occasional flaking to persistent itching, redness, and thick dandruff patches on the scalp. It may also affect the eyebrows, beard, face, and ears. When left untreated, dandruff can trigger temporary hair shedding, acne flare-ups, infections, and severe discomfort.
What Is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
To understand dandruff, one must first understand seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, the underlying medical condition that causes chronic flaking.
This condition occurs when the scalp’s oil glands (sebaceous glands) become overactive, allowing the natural fungus Malassezia to multiply. The imbalance triggers inflammation, leading to flaking, irritation, oiliness, and sometimes temporary hair shedding.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects areas rich in oil-producing glands (sebaceous glands). These include:
- Scalp
- Eyebrows
- Beard
- Sides of the nose
- Ears
- Upper chest
On the scalp, this inflammation speeds up the skin’s natural turnover rate. Instead of shedding gradually, skin cells clump together, resulting in white flakes, yellow, greasy scales, itching, and dandruff patches on the scalp.
What Causes Dandruff?
Understanding what actually triggers dandruff helps patients manage it long-term. While many assume that dandruff is merely a hygiene issue, the reality is far more complex. Multiple biological, lifestyle, environmental, hormonal, and health factors interact to cause seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.
1. Fungal Overgrowth (Malassezia)
The scalp naturally hosts Malassezia yeast. When it grows excessively, it breaks down oils into irritating fatty acids that trigger inflammation.
- Overactivation of the immune response
- Scalp itching and redness
- White or yellow flakes
- Increased sensitivity
This fungal imbalance is the main reason most anti-dandruff shampoos contain antifungal agents.
After understanding fungal involvement, it becomes clear why simple “dry scalp” remedies fail: dandruff is fungal and inflammatory, not just dryness.
2. Excess Sebum (Oil) Production
People with oily scalp produce more sebum, which becomes food for fungus. This explains why oily individuals often need scalp dandruff treatment for oily scalps.
- Hormonal surges
- Stress-related cortisol spikes
- Genetics
- Hot, humid weather
When oil production increases, flakes become thicker and greasier.
This cause emphasises why frequent washing is essential for oily scalp patients and why oiling the scalp may worsen dandruff instead of treating it.
3. Weak or Damaged Scalp Barrier
The skin’s barrier protects against microbes and irritation. When it weakens due to harsh shampoos, pollution, hot water, or chemical treatments, the scalp becomes prone to irritation.
- Burning sensation
- Dry patches
- Increased flaking
- Heightened sensitivity
This shows why dermatologists at Renova always recommend gentle cleansers and barrier-strengthening ingredients
4. Environmental & Seasonal Changes
Changes in temperature and humidity directly influence seborrhea.
- Winter → dry scalp, irritation
- Summer → sweat buildup, fungal proliferation
- Pollution → barrier damage
Seasonal dandruff is extremely common and often mistaken for stress-related hair fall.
5. Skin Conditions
Some individuals have underlying skin disorders that mimic or worsen dandruff.
- Psoriasis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis
This is why understanding the difference between psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis is critical to prevent misdiagnosis.
6. Hair Products and Chemicals
Shampoos with strong fragrances, hair sprays, gels, waxes, or leave-in oils clog pores.
- Product buildup
- Fungal growth
- Irritation
This is why Renova dermatologists stress scalp hygiene and avoidance of comedogenic hair products.
7. Vitamin Deficiencies
Specific nutrients are essential for scalp health.
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B12
- Biotin
- Zinc
Patients asking which vitamin deficiency causes dandruff are often surprised that nutrition plays such a strong role in scalp inflammation.
8. Sweating & Heat Exposure
Scalp sweat triggers fungal growth and weakens the skin barrier.
- Persistent itching
- Burning
- Odor
This also answers the common question: Does sweat cause dandruff? Yes.
9. Hot Water
Hot showers strip natural scalp oil, causing rebound oiliness → worsening dandruff.
Thus, the answer to the question: Does hot water cause dandruff? is a strong YES.
10. Systemic Conditions (Including HIV)
Dandruff is significantly worse in immunocompromised individuals.
- HIV
- Neurological disorders
- Diabetes
- Autoimmune conditions
This highlights the strong correlation between seborrheic dermatitis and HIV.
Important Distinction: Dandruff vs Dry Scalp
Many patients misinterpret their symptoms. Before listing the differences, it is essential to understand that dandruff and dryness are not interchangeable and should be treated differently.
Dandruff vs Dry Scalp
- Dandruff → oily, inflamed, fungal, persistent
- Dry scalp → dehydrated, small, powdery flakes, sensitive
These distinctions explain why dandruff flakes vs dry scalp flakes behave differently, and why moisturising alone cannot cure dandruff.
Understanding this difference ensures patients use the correct treatment rather than worsening their symptoms with ineffective home remedies.
Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Cause Hair Loss?
Before listing the mechanisms, patients must understand that dandruff does not permanently destroy hair follicles. Instead, inflammation, scratching, oil buildup, and fungal imbalance create an unhealthy scalp environment that weakens hair.
How Dandruff Leads to Hair Loss
- Chronic inflammation → weakens hair roots
- Excessive scratching → mechanical breakage
- Oil + flakes clog follicles → reduced growth
- Fungal toxins → disrupt the scalp microbiome
These combined factors cause temporary shedding and thinning.
Thus, the answer to: Can seborrheic dermatitis cause hair loss? is YES, but reversible once inflammation is controlled.
Difference Between Psoriasis and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Many patients mistake thick psoriasis plaques for seborrheic dermatitis flakes. Before listing the differences, it is essential to understand that psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, while dandruff is inflammatory + fungal.
Key Differences
- Psoriasis = thick silver scales
- SD = greasy yellow flakes
- Psoriasis = sharp borders
- SD = diffuse borders
- Psoriasis = immune-driven
- SD = oil & fungus-driven
Distinguishing these ensures accurate treatment and avoids steroid misuse.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Face & Beard Involvement
Dandruff seldom stays confined to the scalp. It often spreads to the:
- Eyebrows
- Beard
- Eyelashes
- Sides of the nose
- Ears
This is why many patients require specialised beard dandruff treatment and facial anti-inflammatory regimens.
Seborrheic Dermatitis and HIV – A Strong Clinical Link
Before listing the reasons, it is important to understand that seborrheic dermatitis worsens dramatically when immunity is weak
Why HIV Worsens Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Weakened immune control of the fungus
- Excess oil production
- Rapid skin turnover
- Higher inflammation
Hence, seborrheic dermatitis scalp and face involvement is widespread in HIV patients and needs coordinated Dermatology + Infectious Disease care.
Symptoms of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Before listing symptoms, note that dandruff symptoms vary widely depending on scalp type, severity, fungal load, and underlying health.
Common Symptoms
- White or yellowish flakes
- Itchy scalp dandruff
- Red, inflamed patches
- Greasy or oily scalp
- Burning sensation
- Scalp odor
- Thick dandruff patches on the scalp
- Hair shedding
- Acne flare-ups
- Eyebrow or beard flakes
Recognising early symptoms allows immediate intervention BEFORE hair fall begins.
Does Dandruff Cause Acne?
Before listing contributing mechanisms, patients should know that dandruff-induced acne is one of the most overlooked forms of forehead breakouts.
How Dandruff Triggers Acne
- Flakes fall and block pores
- Increased sebum spreads to the forehead
- Fungal imbalance affects the skin
- Scratching transfers bacteria
Thus, answering: Does dandruff cause acne? → Yes, and treating the scalp significantly reduces forehead acne.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatment
Treatment is tailored to the underlying cause, severity, scalp type, and patient lifestyle.
1. Medicated Shampoos
Containing:
- Ketoconazole
- Selenium sulfide
- Salicylic acid
- Zinc pyrithione
- Coal tar
These are the foundations of hair dandruff treatment.
2. Topical Medications
- Antifungal creams
- Mild steroid lotions
- Calcineurin inhibitors for facial involvement
- Anti-inflammatory serums
3. Advanced Clinical Therapies
- High-frequency dandruff treatment
- Scalp exfoliation
- Antifungal scalp peels
- Phototherapy for resistant cases
These offer deep follicular cleansing and fungal suppression.
4. Lifestyle & Hygiene Protocol
- Wash hair 2–3 times weekly
- Avoid harsh oils
- Reduce hair gel/wax
- Switch to mild cleansers
5. Seborrheic Dermatitis Diet
Diet influences inflammation. Renova recommends:
- High omega-3 foods
- Probiotics
- Low sugar
- Avoiding processed food
- Zinc-rich foods
This helps reduce flare-ups.
6. Home Remedies (Supported by Dermatology)
- Overnight dandruff treatment with the prescribed antifungal lotion
- Warm water + mild shampoo
- Tea tree oil preparations (safe, diluted)
7. Specialised Treatments
- Beard dandruff treatment
- Hairfall and dandruff treatment
- Oily scalp dandruff treatment
- Best hair treatment for dandruff personalised per scalp type
Seborrheic Dermatitis Diet
Before listing dietary recommendations, it is crucial to understand that diet affects inflammation, oil production, and overall skin health.
Foods That Help Reduce Flare-Ups
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Probiotics
- Zinc-rich foods
- Vitamin B-rich foods
- Hydrating fruits and vegetables
These foods support the scalp barrier and reduce inflammation internally.
Overnight Dandruff Treatment
Before listing options, note that overnight therapies help medications penetrate deeper into the scalp.
Recommended Overnight Treatments
- Antifungal lotions
- Zinc serums
- Keratolytic preparations
These treatments allow deeper absorption, improving results faster than daytime application alone.
Prognosis
Seborrheic dermatitis usually comes and goes, with periods of flare-ups and periods of clear skin. It isn’t dangerous, doesn’t affect your overall health, and is highly manageable with the proper treatment. Most people notice improvement quickly once they start using the correct medicated shampoos or prescription creams.
Home Care Tips to Prevent Dandruff
Before listing recommendations, understand that home care is crucial for long-term maintenance.
Effective Home Care Tips
- Avoid hot water
- Reduce sweating
- Use gentle shampoos
- Avoid sharing combs
- Do not scratch
- Change pillow covers frequently
Renova Hospitals Hyderabad – Expert Dermatology Care
Our dermatology centres across Banjara Hills, Secunderabad, Kompally, and Warangal provide comprehensive assessment and customised dandruff treatment in Hyderabad using both medical and advanced clinical techniques.
FAQs
1. Is seborrheic dermatitis permanent?
No. It isn’t permanent but is chronic. Flare-ups come and go, and symptoms stay controlled with regular seborrheic dermatitis treatment.
2. Can seborrheic dermatitis cause hair loss?
Yes, temporarily. Inflammation and scratching can weaken roots, but hair regrows once the scalp heals.
3. What’s the difference between dandruff and dry scalp?
Dandruff = oily, inflamed scalp with fungal overgrowth.
Dry scalp = lack of moisture with small, dry flakes.
4. Which shampoo works best?
Choose shampoos with ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione, salicylic acid, or coal tar. If flakes persist, see a dermatologist.
5. When should I see a doctor?
If dandruff doesn’t improve, spreads to your face or beard, causes redness or hair thinning, or if you suspect severe seborrheic dermatitis of scalp.