By Renova Hospitals
December 10, 2025
Gallstones: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment and Surgery – Complete Medical Guide by Renova Hospitals, Hyderabad
When a patient experiences repeated episodes of upper abdominal pain, nausea, or shoulder pain after meals, timely evaluation from a gallstone specialist becomes crucial.
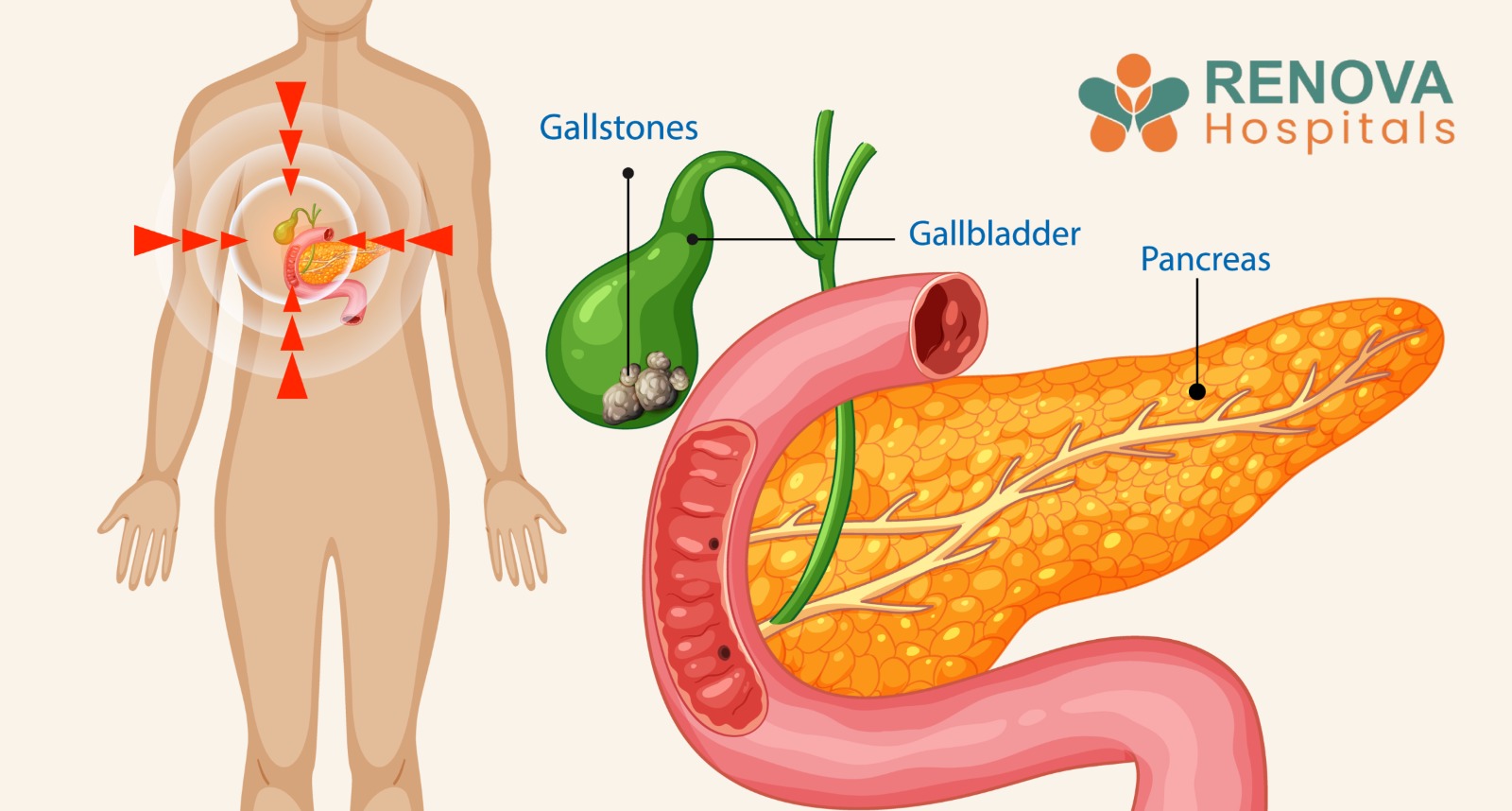
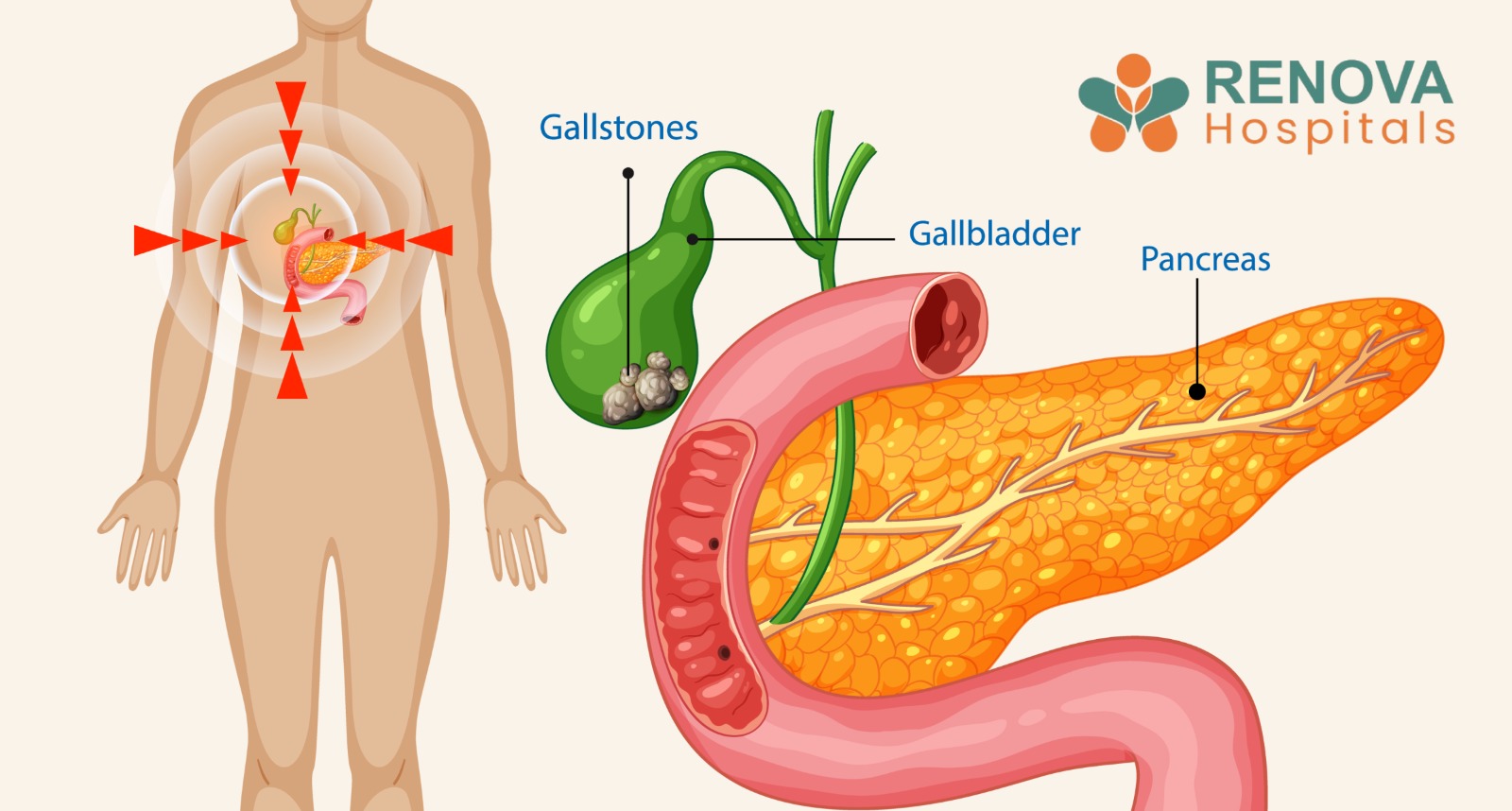
- Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile stored in the gallbladder.
- Stones vary in size from a grain of sand to several centimetres.
- Symptomatic gallstones require treatment to prevent severe complications.
- Gallstone removal surgery remains the most reliable long-term cure.
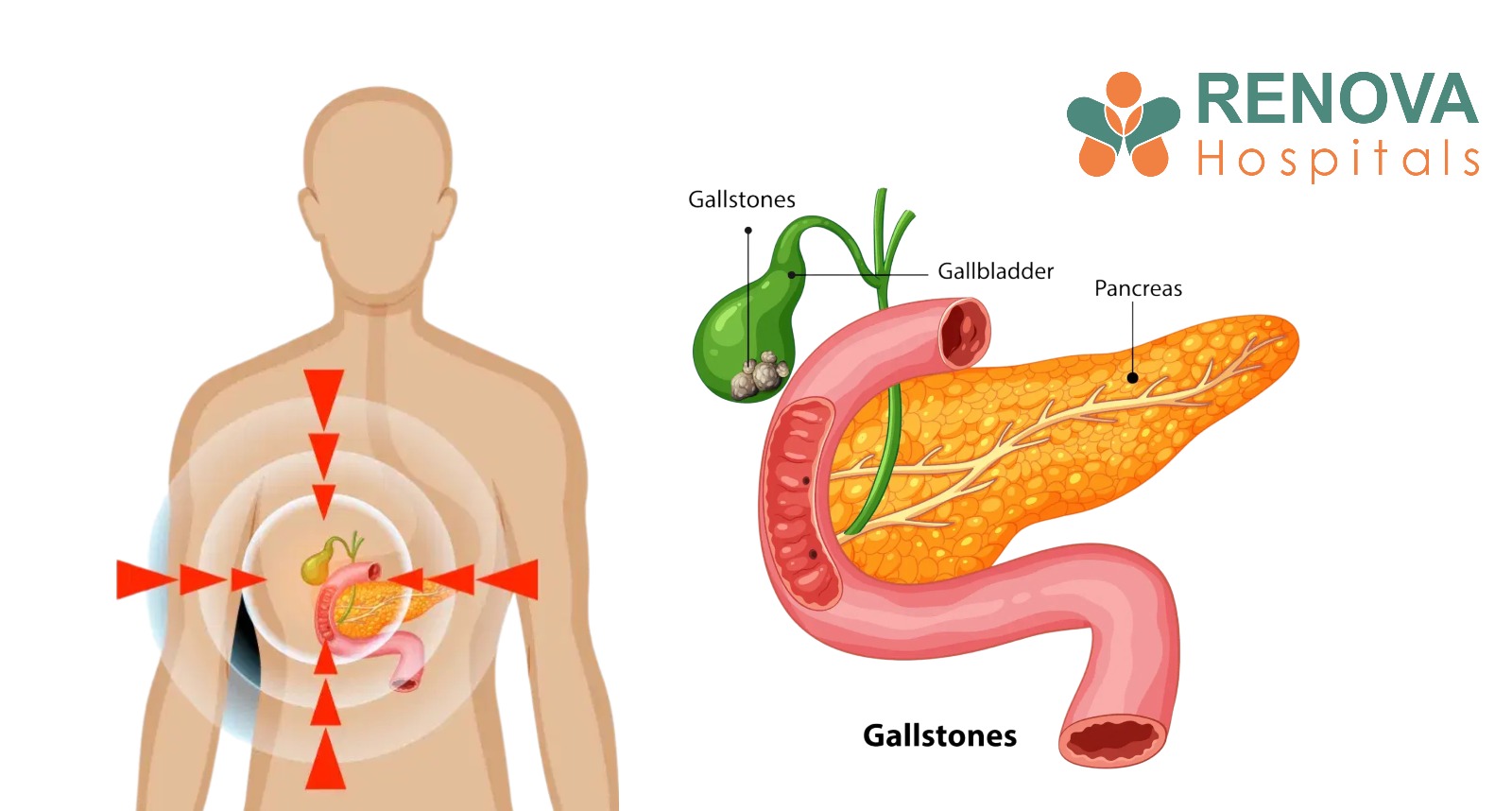
What Are Gallstones?
Types of Gallstones
1. Cholesterol Stones
- Most commonly seen in adults.
- Develop due to excess cholesterol in the bile.
- Often associated with obesity, a fatty diet, a sedentary lifestyle, or hormone changes.
- Formed due to excess bilirubin.
- Frequently linked to liver disease, hemolytic anaemia, or chronic infections.
- Typically smaller but more numerous.
- Contains cholesterol and pigment components.
- Common in chronic gallbladder inflammation cases.
How Serious Are Gallstones?
- Pain becomes recurrent.
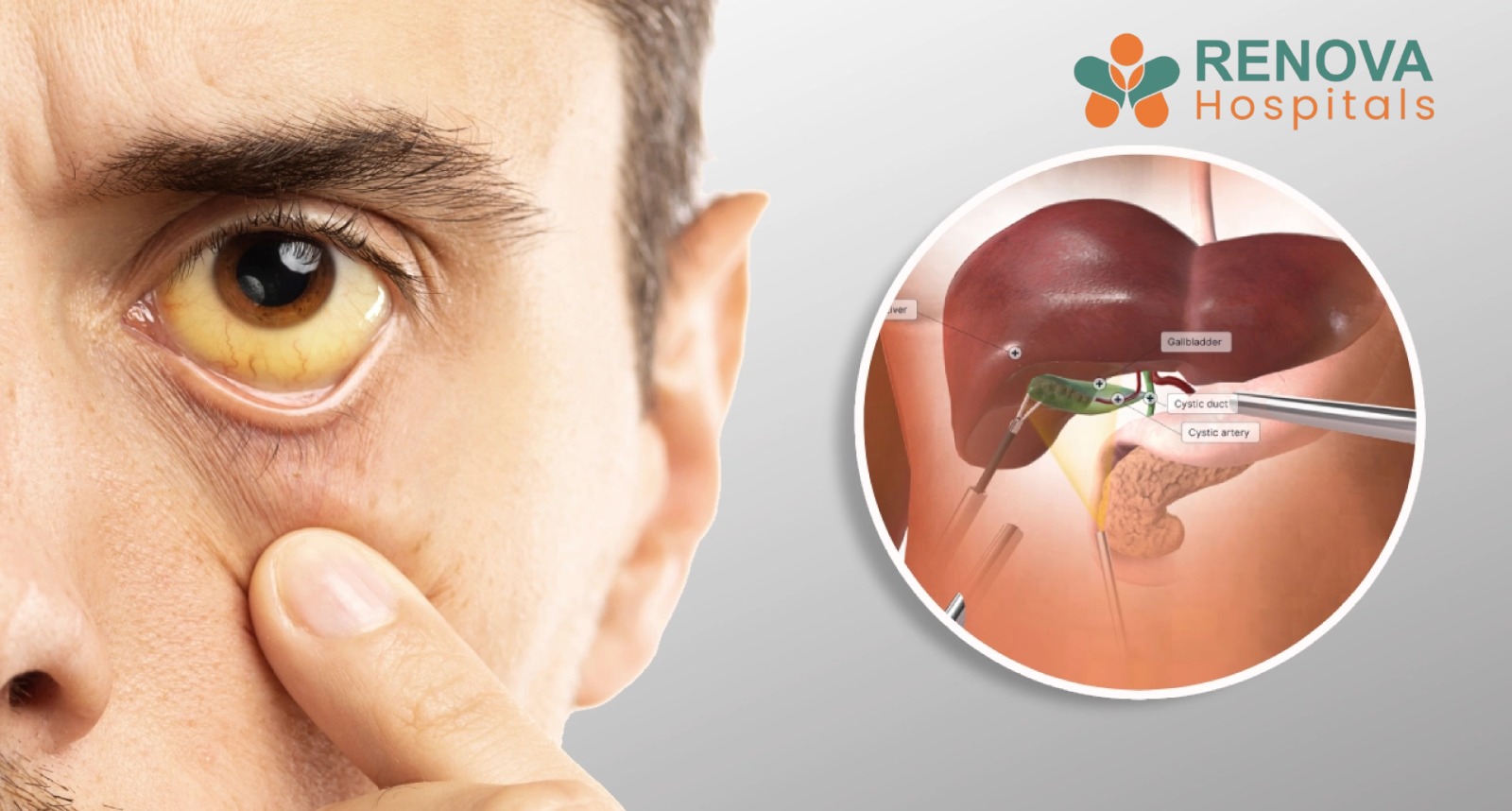
- Jaundice develops.
- Fever accompanies abdominal pain.
- Vomiting persists.
- Blood tests indicate elevated liver enzymes or infection.
How Common Are Gallstones?
- Higher in women, especially during reproductive years.
- Increased risk during gallstones and pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
- More common in individuals who are obese or who rapidly lose weight.
- Strong familial and genetic influence.
Symptoms and Causes
- Sudden severe pain in the right upper abdomen.
- Pain triggered after high-fat meals.
- Persistent nausea or vomiting.
- Indigestion, bloating, early satiety.
- Gallstones and back pain radiating to shoulder or between shoulder blades.
- Dark urine and pale stools due to altered bilirubin flow.
- Fever and chills indicating infection.
- Jaundice suggesting obstruction.
What Does Gallstone Pain Feel Like?
- Sharp, throbbing, cramping, and squeezing abdominal pain.
- Pain severe enough to interrupt sleep.
- Pain aggravated by deep breathing or movement.
- Episodes often occurring at night or after heavy meals.
- Pain subsiding temporarily only to recur later.
Where Is Gallstone Pain Located?
- Right shoulder
- Upper back
- Area between the shoulder blades
- Central abdomen or chest
Gallstones in Women and Pregnancy
- Estrogen increases cholesterol in bile.
- Progesterone slows gallbladder emptying.
- Reduced movement causes stagnation and stone formation.
What Triggers Gallstone Pain?
- Heavy, oily or spicy meals
- Eating large portions at once
- Skipping meals and overeating later
- High cholesterol and a low-fibre diet
- Rapid weight loss programs
- Dehydration and prolonged fasting
- Alcohol consumption in some individuals
- Pain is continuous and lasts more than 6 hours.
- Fever accompanies abdominal pain.
- Vomiting persists.
- Skin or eyes turn yellow.
- Abdominal swelling with tenderness appears.
Possible Complications of Untreated Gallstones
If a stone blocks the bile ducts, the following complications may occur:
- Acute cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation)
- Pancreatitis caused by duct obstruction
- Cholangitis (infection of the bile ducts)
- Hepatitis or liver damage
- Empyema or perforation of the gallbladder
- Sepsis, which is life-threatening
What Causes Gallstones?
- Excess cholesterol exceeds bile salt capacity.
- High bilirubin levels due to hemolytic diseases.
- Reduced bile flow, causing stagnation.
- Chronic infections in the biliary system.
- High-fat diet with low fibre intake.
- Being overweight or sedentary.
- Very rapid weight loss after dieting or surgery.
- Women more than men.
- Individuals above 40 years.
- Family history of gallstones.
- Gallstones and pregnancy.
- Obesity or sudden weight loss.
- High-cholesterol dietary habits.
- Diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
- Liver disease or hemolytic disorders.
- Long-term birth control pill usage
Diagnosis and Tests
- Ultrasound Abdomen
- First-line imaging.
- Detects stones in the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography)
- Detailed view of the biliary tree.
- Recommended for ductal stones.
- HIDA Scan
- Evaluates gallbladder function.
- Useful in acute cholecystitis.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound
- Detects small stones not visible in surface ultrasound.
- ERCP
- Diagnostic and therapeutic.
- Can remove stones in the common bile duct.
Blood tests to evaluate:
- Liver function tests
- Bilirubin levels
- Pancreatic enzymes
- Inflammatory markers
Treatment depends on size, symptoms, and complications.
Medication for Gallstones
Medical therapy is limited. Ursodeoxycholic Acid may help dissolve small cholesterol stones, but requires long-term use, and recurrence risk is high. Medication for gallstones is generally recommended only when surgery is not possible temporarily.
Limitations:
- Works only for small stones.
- Takes months to years.
- Does not guarantee a permanent cure.
Gallstone Removal Surgery
- Prevents recurrent attacks permanently.
- Reduces risk of infection and pancreatitis.
- Short hospital stay.
- Faster recovery with minimal scarring.
Post-Surgical Recovery
- Discharge within 24 to 48 hours in most cases.
- Resume light activities in a few days.
- Full recovery in 1 to 2 weeks.
- Normal diet gradually reintroduced.
- Long-term dietary restrictions are usually minimal.
Diet and Lifestyle Management
- Fried foods, excessive oils.
- Red meat, liver, high-fat dairy.
- Bakery products, refined flour.
- Foods rich in trans fats.
- Processed meats.
- Cream-based gravies and desserts.
- High-fibre vegetables and whole grains.
- Lean proteins like fish and chicken.
- Brown rice, oats, millets.
- Adequate hydration.
- Moderate use of healthy fats like olive oil.
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Avoid rapid weight loss and crash diets.
- Regular physical activity.
- Avoid alcohol if it triggers symptoms.
- Eat small, frequent meals instead of heavy servings.
Professional consultation is necessary when:
- Experiencing repeated right upper abdominal pain.
- Pain wakes you up at night.
- Jaundice develops.
- Fever accompanies abdominal pain.
- Pain radiates to the back or right shoulder.
- Symptoms worsen after eating fatty meals.
Prognosis / Outlook After Treatment for Gallstones
Patients who undergo timely treatment for gallstones, especially through laparoscopic gallbladder removal, generally have an excellent prognosis. Once the gallbladder is removed, stones do not recur because the organ responsible for stone formation is no longer present.
- Most patients resume normal activity within 1 to 2 weeks after surgery.
- Digestive function remains normal in the long term, as bile flows directly to the intestine.
- A small percentage of patients may develop mild loose stools initially; this usually improves naturally or with diet adjustments.
- Chronic complications such as recurrent infection, pancreatitis, or bile duct obstruction largely disappear after surgery.
- Patients with untreated gallstones have a higher chance of emergencies, including cholecystitis, cholangitis, or pancreatitis, which can be severe.
- Prognosis is significantly better when intervention is done early rather than waiting for complications.
- Asymptomatic gallstones may require only monitoring, but symptomatic stones have a high chance of recurring attacks.
- Quality of life returns to normal.
- No major dietary restrictions are required after recovery.
- No impact on lifespan when treated appropriately.
- Patients usually do not require repeat procedures.
Gallstone Treatment at Renova Hospitals, Hyderabad
Facilities available:
- Experienced gastroenterologists and biliary surgeons.
- 24/7 emergency care.
- Advanced imaging, including Ultrasound, MRCP, and ERCP.
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic gallbladder removal.
- Post-surgery dietary and recovery monitoring.
FAQs
Gallstones rarely disappear naturally. Most remain unchanged or grow over time.
2. Are medications effective for treating gallstones?
Medication for gallstones works only for small cholesterol stones and requires a long duration. Surgery remains the most reliable option.
3. When is surgery necessary?
Surgery is recommended if symptoms begin, stones cause blockage, infection occurs, or the risk of complications increases.
4. Can gallstones cause back or shoulder pain?
Yes. Referred nerve pain often results in gallstones and back pain or right shoulder discomfort.
5. What if gallstones are found during pregnancy?
Treatment depends on severity. Diet modification and monitoring may be sufficient. Emergency cases require specialist-managed treatment.
6. Are gallstones and kidney stones the same?
No. Gallstones vs kidney stones differ in location, formation, symptoms and treatment approach.
7. How long does recovery take after surgery?
Most patients resume routine life in 1 to 2 weeks after laparoscopic removal.
8. Can diet prevent gallstones?
Diet reduces risk but does not remove existing stones. Balanced nutrition and weight management help prevent.
9. Can gallstones be left untreated if no pain exists?
Asymptomatic stones may remain under observation, but symptomatic stones require treatment to prevent complications.
10. Is life normal after gallbladder removal?
Yes. Bile flows directly into the intestine, and digestion continues normally with minimal long-term dietary adjustments.
Category
- Joint Replacement
- Joint Replacement
- Joint Replacement