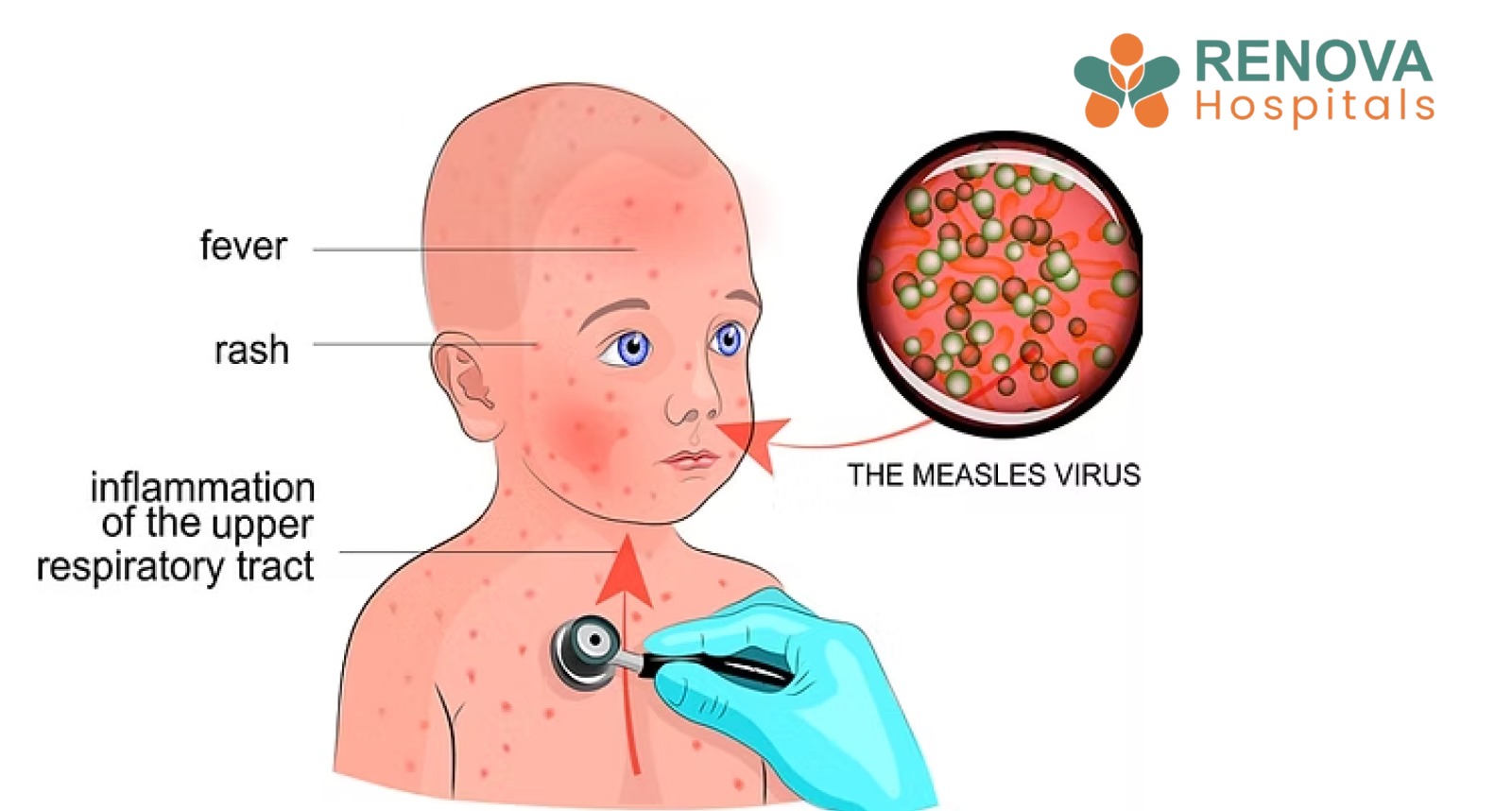
Fever is one of the most frequent health concerns in childhood. Almost every parent has faced sleepless nights worrying over a thermometer reading. In most cases, fever is short-lived and reassuringly linked to common viral infections. However, when fever persists beyond what is expected, it ceases to be a routine childhood illness and becomes a significant medical signal.
Prolonged fever is not just “fever that lasts longer.” It is the body’s sustained alert that something deeper may be occurring. Unfortunately, prolonged fever in children is often underestimated, masked by repeated medications, or normalised as “weak immunity” or “seasonal illness.” This delay can have serious consequences.
This comprehensive guide explains what is prolonged fever, its symptoms, prolonged fever causes, evaluation strategies, prognosis, and why early specialist care, especially at a centre like Renova Hospitals, can make a life-changing difference.
Understanding Fever: A Protective Response, Not a Disease
Fever is a natural immune response. When the body detects infection or inflammation, it raises its temperature to slow down invading organisms and activate immune cells. Short-term fever is often beneficial.
However, the immune system is not designed to remain in a prolonged state of activation. When fever continues beyond its expected duration, it suggests:
- Ongoing infection
- Uncontrolled inflammation
- Immune dysregulation
- Or, in rare cases, malignancy
This is why fever duration is clinically more important than fever height.
What Is Prolonged Fever in Children?
Parents frequently ask doctors what is prolonged fever and how it differs from a normal illness.
From a medical perspective, fever is considered prolonged when:
- Fever lasts more than 7 days, or
- Fever continues despite treatment of an apparent infection, or
- Fever keeps recurring without a clear diagnosis
This definition applies even when temperatures are mild. A prolonged low-grade fever, where the child appears “almost normal” but never fully well, can be particularly deceptive and easily ignored.
Why Prolonged Fever Should Never Be Taken Lightly
Children are resilient, but their immune systems are still developing. Persistent fever can:
- Delay growth and weight gain
- Affect hydration and nutrition
- Cause fatigue, irritability, and poor concentration
- Mask serious underlying diseases
Repeatedly suppressing fever without investigating the cause may give temporary relief while allowing the disease to progress silently.
Prolonged Fever in Infants: A High-Risk Situation
Prolonged fever in infants deserves special attention. Infants, especially under one year of age:
- Cannot verbalise symptoms
- May not localise infections
- Can deteriorate rapidly
Even a mild fever lasting 24–48 hours or more in infants can signal a serious bacterial infection, bloodstream infection, or meningitis. In this age group, prolonged fever is never considered normal.
Patterns of Prolonged Fever Doctors Look For
Doctors don’t just ask how long the fever lasts, they also assess how it behaves.
Common patterns include:
- Continuous fever: temperature remains elevated throughout the day
- Intermittent fever: fever spikes and returns to normal
- Relapsing fever: fever disappears for days and returns
Each pattern provides clues for the differential diagnosis of prolonged fever.
Symptoms That Often Accompany Prolonged Fever
Fever is rarely isolated. Associated symptoms help narrow down causes.
General Symptoms
- Persistent tiredness
- Irritability or behavioural changes
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss or poor growth
Respiratory Symptoms
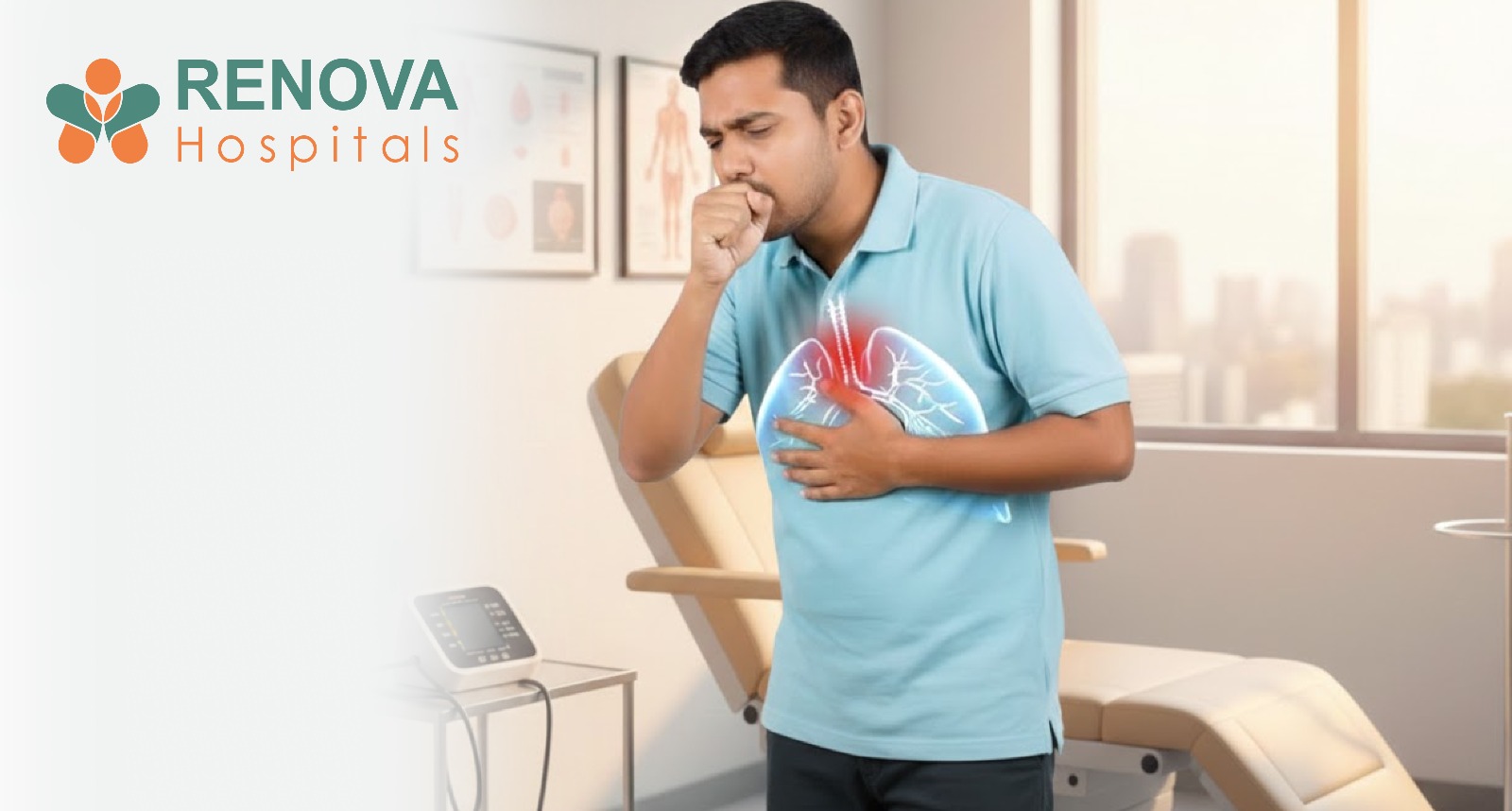
Children with prolonged fever with cough or prolonged fever and cough may have:
- Persistent or worsening cough
- Breathlessness
- Chest pain
- Night sweats
These symptoms raise concern for chronic lung infections, including tuberculosis.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
- Recurrent abdominal pain
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal swelling
Musculoskeletal and Skin Symptoms
- Joint pain or swelling
- Rashes
- Red eyes or cracked lips
These may point toward inflammatory or autoimmune conditions.
Prolonged Fever Causes: Infectious Conditions
Infections remain the most common prolonged fever in children.
Bacterial Infections
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid fever
- Urinary tract infections
- Bone and joint infections
- Hidden abscesses
Children with prolonged fever and cough are carefully evaluated for pulmonary infections.
Viral Infections With Long Courses
Certain viral infections do not follow the usual “3–5 day” pattern and can cause fever lasting weeks:
- Epstein–Barr virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Post-viral inflammatory states
Causes of Prolonged Fever in Child: Non-Infectious Conditions
When infections are ruled out, doctors consider other causes of prolonged fever in a child.
Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders
These often present with prolonged low-grade fever, rashes, joint pain, or swollen lymph nodes.
Malignancies (Uncommon but Serious)
Cancers such as leukaemia and lymphoma may initially present only with unexplained prolonged fever, along with:
- Pallor
- Easy bruising
- Frequent infections
Early recognition significantly improves outcomes.
Miscellaneous Causes
- Drug-induced fever
- Metabolic disorders
- Immune deficiencies
Prolonged Fever Differential Diagnosis: A Structured Medical Approach
Prolonged fever differential diagnosis involves systematically ruling out multiple disease categories rather than guessing.
Doctors classify causes into:
- Infectious
- Inflammatory/autoimmune
- Malignant
- Miscellaneous
This approach prevents missed diagnoses and unnecessary treatments.
Diagnostic Evaluation: What Parents Should Expect
There is no single test that explains all cases of prolonged fever.
Step 1: Detailed History
- Duration and pattern of fever
- Exposure to infections
- Travel history
- Vaccination status
Step 2: Physical Examination
- Growth assessment
- Lymph nodes
- Joint and skin examination
Step 3: Laboratory Tests
- Blood counts
- Inflammatory markers
- Liver and kidney tests
- Urine analysis
Step 4: Imaging
- Chest X-ray (important in prolonged fever with cough)
- Ultrasound or advanced imaging if needed
Does Reducing Fever Prolong Illness?
A common myth parents worry about is: Does reducing fever prolong illness?
Medical evidence is clear:
- Fever-reducing medicines do not prolong infection
- They improve comfort, hydration, and feeding
- They do not interfere with immune recovery
The danger lies not in treating fever, but in ignoring persistent fever without evaluation.
Treatment Principles in Prolonged Fever
Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause:
- Targeted antibiotics for confirmed bacterial infections
- Antivirals or supportive care for viral causes
- Immunomodulatory therapy for inflammatory conditions
Random or repeated antibiotic use without diagnosis is avoided, as it can delay accurate evaluation.
Prognosis: What Happens After Diagnosis?
The prognosis of prolonged fever depends on:
- Underlying cause
- Child’s age
- Speed of diagnosis
Positive Outcomes
- Most children recover completely once the cause is identified
- Early treatment prevents complications
Risks of Delay
- Disease progression
- Organ damage
- Longer hospitalisation
- Emotional stress for families
Emotional Impact on Families
Prolonged fever affects not only the child but the entire family. Repeated uncertainty, hospital visits, and lack of answers can cause anxiety and fatigue. Clear communication and structured evaluation are essential for reassurance and trust.
When Parents Should Seek Immediate Care
Seek urgent medical attention if a prolonged fever is associated with:
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent vomiting
- Poor feeding
- Weight loss
- Seizures
- Fever in infants lasting more than 24–48 hours
Parents instincts matter, if something feels wrong, it deserves attention.
Prolonged Fever Needs Expertise, Not Assumptions
If your child has:
- Prolonged fever
- Prolonged fever with cough
- Prolonged low-grade fever
- Prolonged fever in infants
- Fever that keeps returning despite treatment
do not wait for it to “settle on its own.”
At Renova Hospitals, experienced paediatric and medical teams follow structured, evidence-based protocols to identify the cause of prolonged fever early, accurately, and safely. Timely evaluation can prevent complications, reduce unnecessary treatments, and provide clarity when families need it most.
Persistent fever is the body’s message.
Listening early at Renova Hospitals can protect your child’s future health.