By Renova Hospitals
February 21, 2026
Skin Cancer: Symptoms, Stages and Modern Treatment Options in Hyderabad
Key Takeaways
- Skin cancer is the most common cancer worldwide, largely driven by ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure.
- It is broadly classified into melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC).
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type, while melanoma is the most aggressive.
- When detected early, survival rates are extremely high often close to 99%.
- Routine skin checks and proper sun protection can greatly lower the risk.
- Modern treatments such as Mohs surgery, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and precision radiation are available in Hyderabad.
What Is Skin Cancer?
Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is classified into two major categories:
- Most common skin cancer worldwide
- Appears as a pearly bump, pink patch, or non-healing sore
- It usually does not spread to other organs, but if ignored, it can damage nearby skin and tissue.
- It tends to behave more aggressively than basal cell carcinoma.
- Appears as a red, scaly patch or crusted lesion
- Can spread to lymph nodes if untreated
Main Subtypes:
- Superficial Spreading Melanoma (60–70%)
- Nodular Melanoma
- Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
- Acral Lentiginous Melanoma (common in darker skin tones)
What Causes Skin Cancer?
- Fair skin that burns easily
- History of repeated sunburns
- Age above 50 years
- Male gender
- Family history of skin cancer
- Weakened immune system (HIV, transplant patients)
- Radiation exposure
- Arsenic exposure
- Certain genetic syndromes
Skin Cancer Statistics: Global and Indian Perspective
- Skin cancer accounts for 1 in 3 diagnosed cancers.
- Non-melanoma skin cancers exceed 1000000 new cases annually.
- Melanoma cases continue to rise worldwide.
- Higher UV exposure
- Occupational sun exposure
- Lifestyle changes
- Increased awareness and improved diagnostic facilities
Regular screening plays an important role in preventing serious complications.
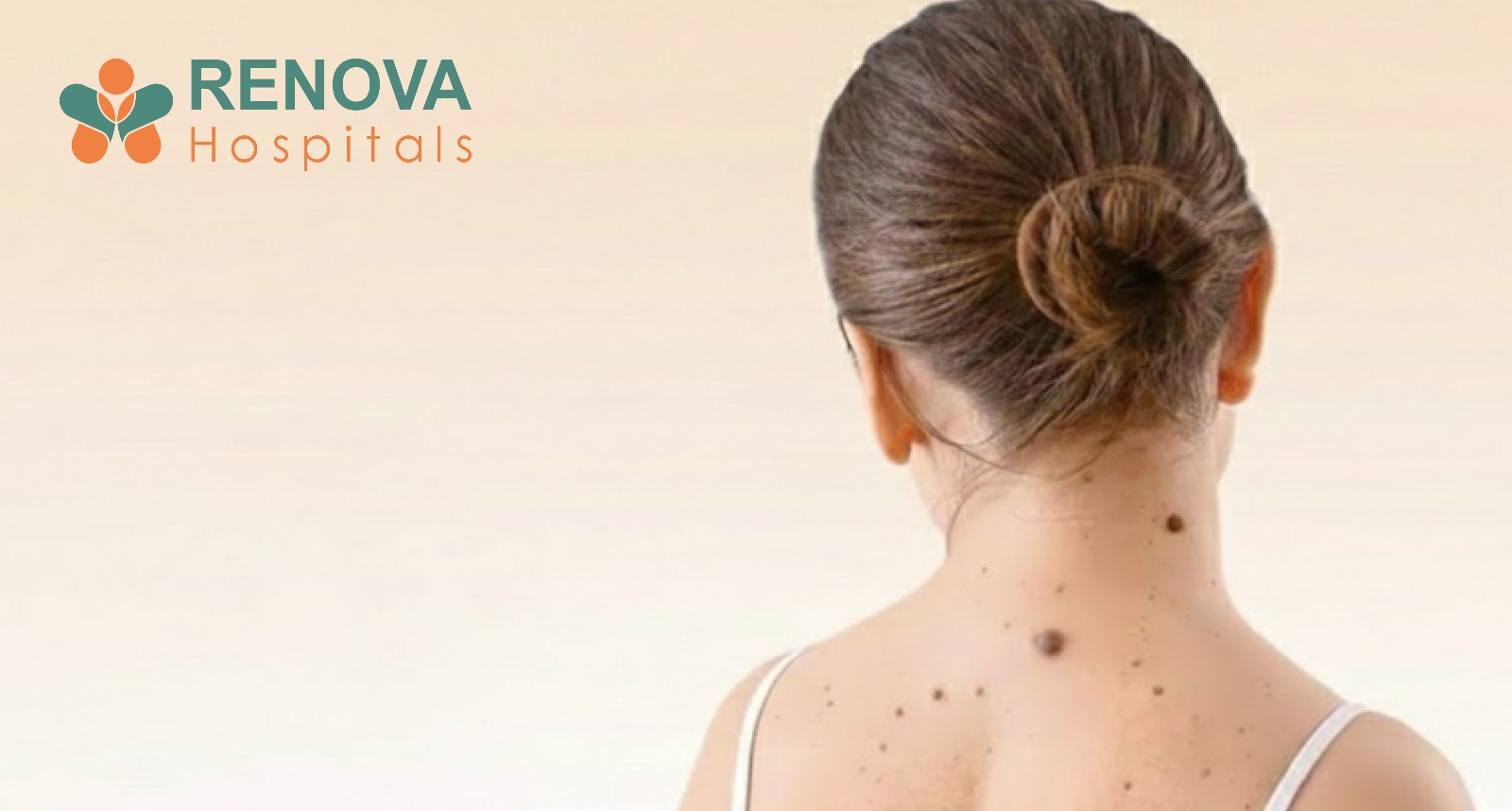
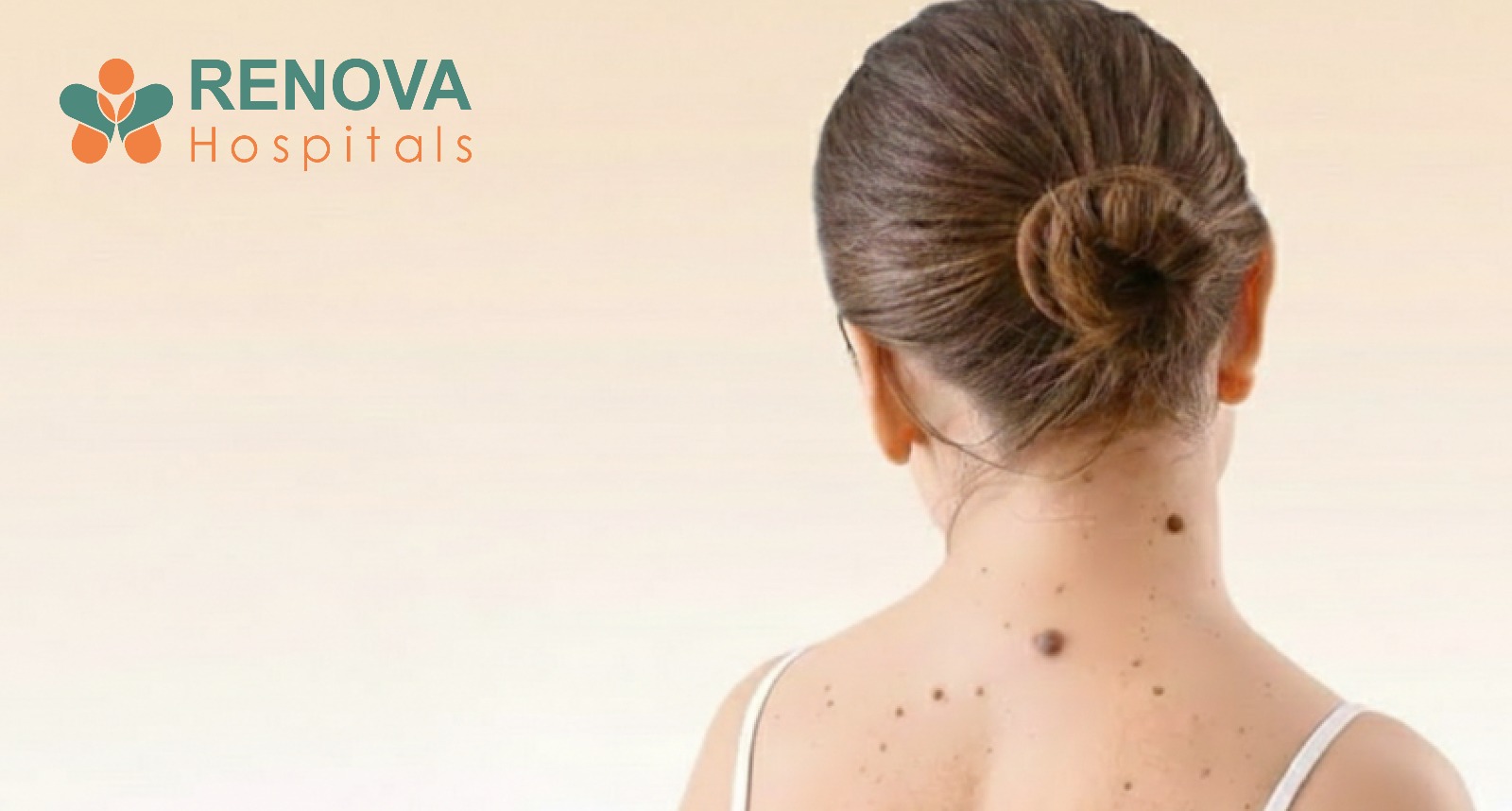
What Are the Early Signs of Skin Cancer?
Use the ABCDE Rule for Melanoma:
- A – Asymmetry
- B – Border irregularity
- C – Color variation
- D – Diameter >6 mm
- E – Evolving (changing shape or size)
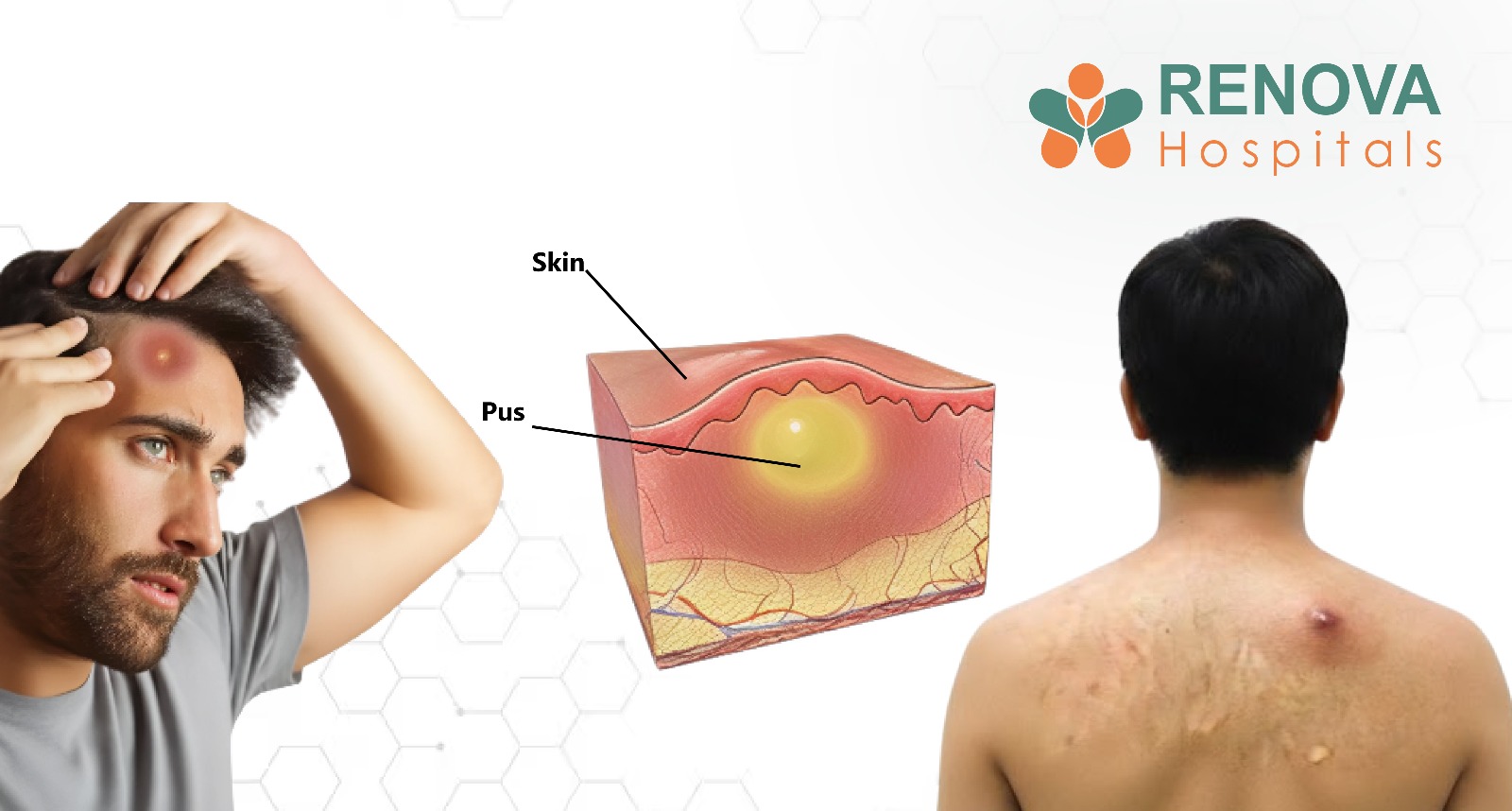
- A sore that does not heal
- A pearly or waxy bump
- Scaly red patches
- Bleeding or crusting lesions
- Rapidly growing dark mole
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
- Clinical skin examination
- Dermoscopy
- Skin biopsy (shave, punch, incisional, or excisional)
- Histopathological evaluation
- Breslow thickness
- TNM classification
- Lymph node involvement
- Imaging (CT, PET, ultrasound if advanced)
Stages of Skin Cancer
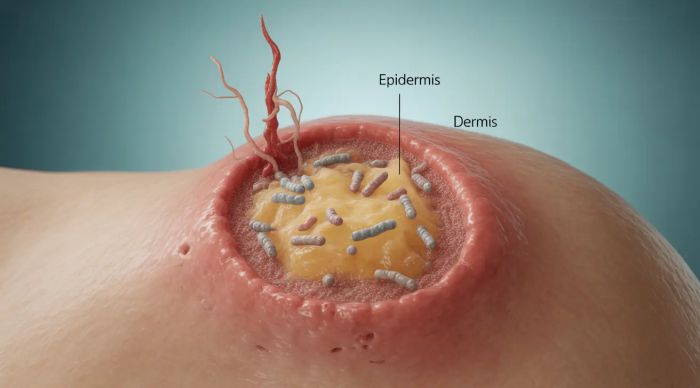
- Stage 0: In situ (confined to epidermis)
- Stage I-II: Localized, increasing thickness
- Stage III: Spread to lymph nodes
- Stage IV: Metastasis to distant organs
Treatment Options for Skin Cancer in Hyderabad
- Simple excision
- Mohs micrographic surgery
- Curettage and electrodesiccation
- Cryotherapy
2. Radiation Therapy
- PD-1 inhibitors (Cemiplimab, Pembrolizumab)
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- BRAF inhibitors
- MEK inhibitors
- Hedgehog pathway inhibitors (Vismodegib for BCC)
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented?
- Avoid direct sun exposure between 10 AM to 4 PM
- Use SPF 30+ broad-spectrum sunscreen
- Reapply every 2 hours
- Wear protective clothing and hats
- Avoid tanning beds
- Conduct monthly self-exams
- Annual dermatologist screening in sunny regions like Hyderabad
- Immunotherapy now the first-line for advanced melanoma
- Targeted therapy for BRAF mutations
- Alpha DaRT therapy trials for SCC
- AI-assisted dermoscopy for early detection
- Improved precision radiation therapy
Ongoing research is exploring:
- Cancer vaccines
- Genetic profiling
- Tele-dermatology for rural India
Why Early Detection Matters
- Higher cure rates
- Less aggressive treatment
- Lower risk of recurrence
- Better cosmetic outcomes
- Improved long-term survival
Medical Disclaimer
Category
- Joint Replacement
- Joint Replacement